chapter two
Materiality assessment

Focus starts with
understanding materiality.

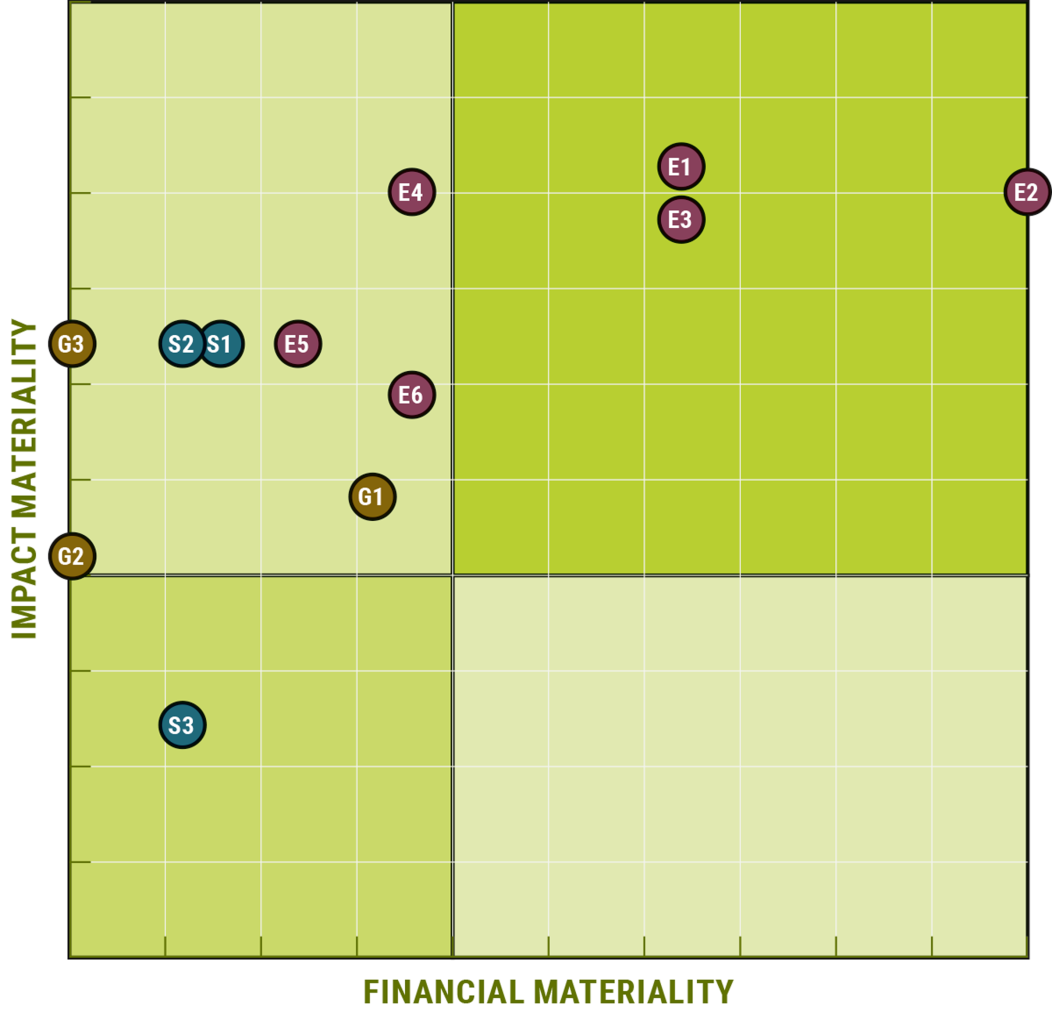
Our materiality analysis evaluates both impact materiality (inside-out) and financial materiality (outside-in). This dual approach ensures that we consider the effects of our operations on the environment and society, as well as the financial implications of ESG factors on our business. By doing so, we can develop a holistic sustainability strategy that addresses the most critical issues.
The methodology for our materiality analysis involved several key steps:
1. Identification of ESG Topics: We identified key ESG areas to be analysed, including Environment (climate change, pollution, water, biodiversity, circular economy), Social (workforce, value chain workers, communities, consumers), and Governance (business conduct).
2. Stakeholder Engagement: We engaged with a diverse group of stakeholders, including customers, suppliers, employees, NGOs, and the Supervisory Board. Next to engaging with customers and suppliers, we analysed public sustainability reports and collected employee feedback across business units.
3. Risk and Opportunity Assessment: We assessed and validated risks, opportunities, and impacts through stakeholder consultations. This process helped us understand the significance of each ESG topic and its relevance to our business and stakeholders.
4. Development of Materiality Matrix: We developed a materiality matrix, which visually represents the priority of identified topics based on their impact and importance.
Stakeholder involvement was an important part of our materiality analysis. We used various methods to gather input, including surveys, interviews, and desk research. The feedback from stakeholders provided valuable insights into their concerns and expectations, which helped us refine our sustainability strategy.
Our materiality assessment resulted in a list of material topics. These topics form the basis of our sustainability strategy and report. To create additional focus, three United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (12, 13, and 17) are selected and form the ‘Faber Development Goals’. We aim to significantly contribute to these SDGs.
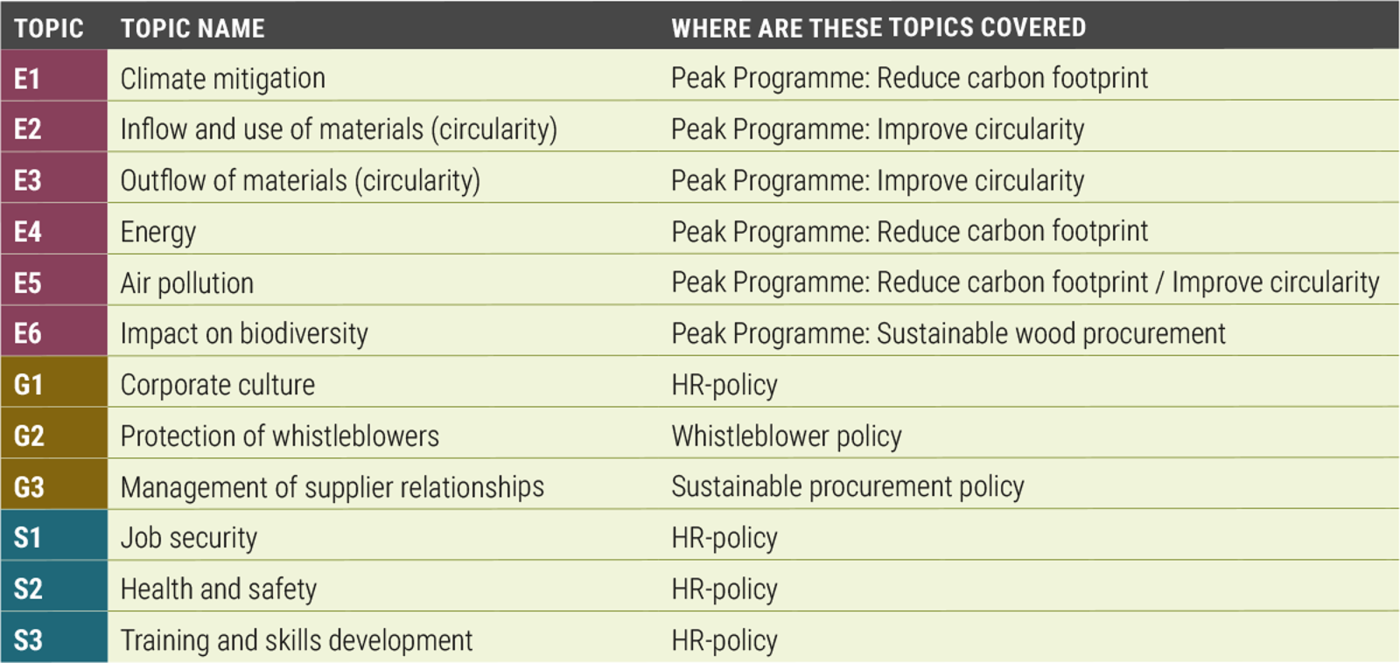
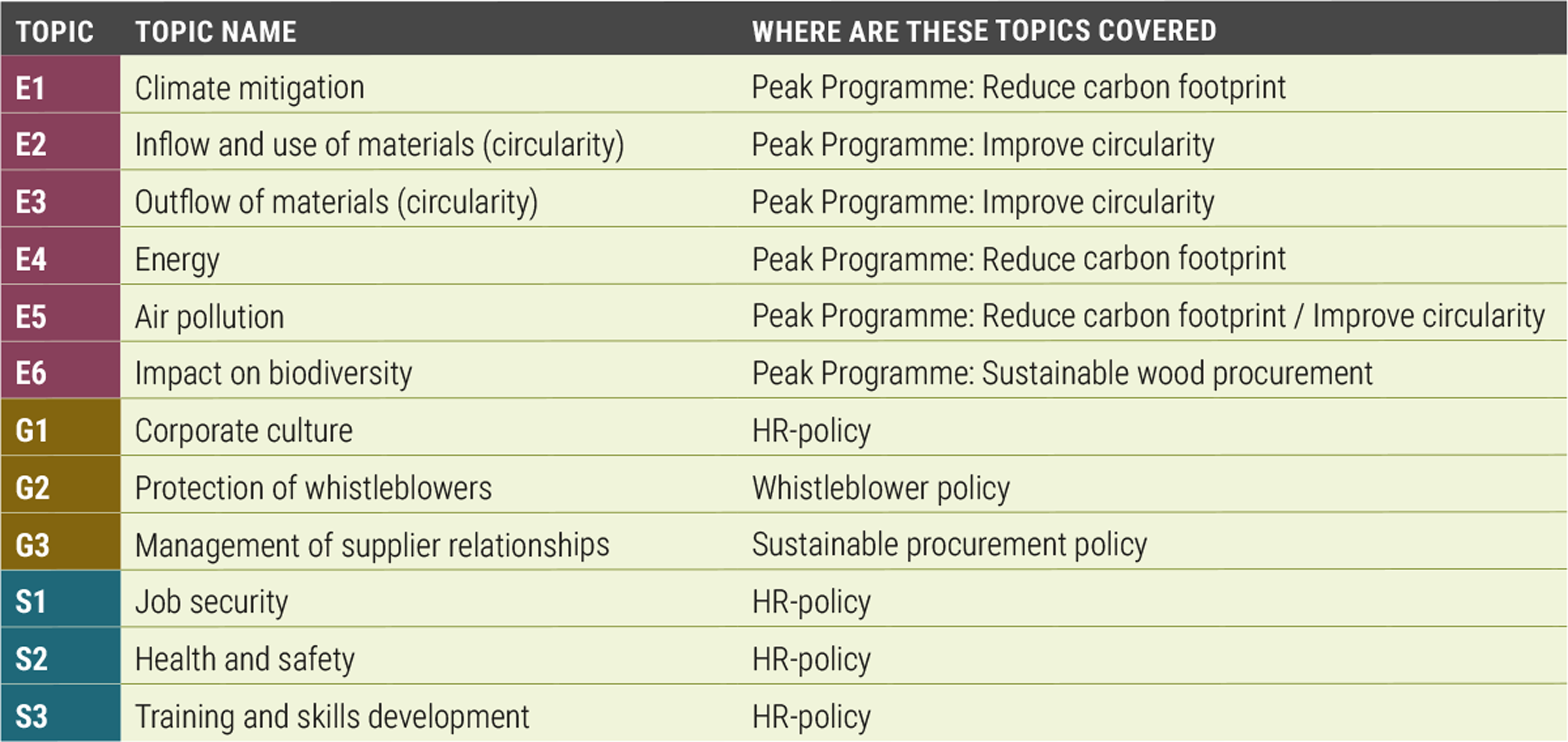
The materiality assessment has provided us with a clear understanding of the most critical sustainability topics for our organization and stakeholders. These topics are integrated into our sustainability strategy and guide our actions to achieve our goals. By focusing on the identified material topics, we can effectively manage risks, capitalize on opportunities, and enhance our overall sustainability performance. In the ESG overview we have also highlighted in which policies these topics are addressed.
A Double Materiality Assessment (DMA) is essential for identifying key Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors impacting both us and our stakeholders. It helps us prioritise sustainability issues, manage risks, and seize opportunities. We conducted a materiality assessment in 2022 and repeated it in 2024 to verify the results of the initial analysis and to align with CSRD requirements.
Sustainability Progress Report | 2024
chapter two
Materiality assessment
Focus starts with
understanding materiality.


A Double Materiality Assessment (DMA) is essential for identifying key Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors impacting both us and our stakeholders. It helps us prioritise sustainability issues, manage risks, and seize opportunities. We conducted a materiality assessment in 2022 and repeated it in 2024 to verify the results of the initial analysis and to align with CSRD requirements.
Sustainability Progress Report | 2024
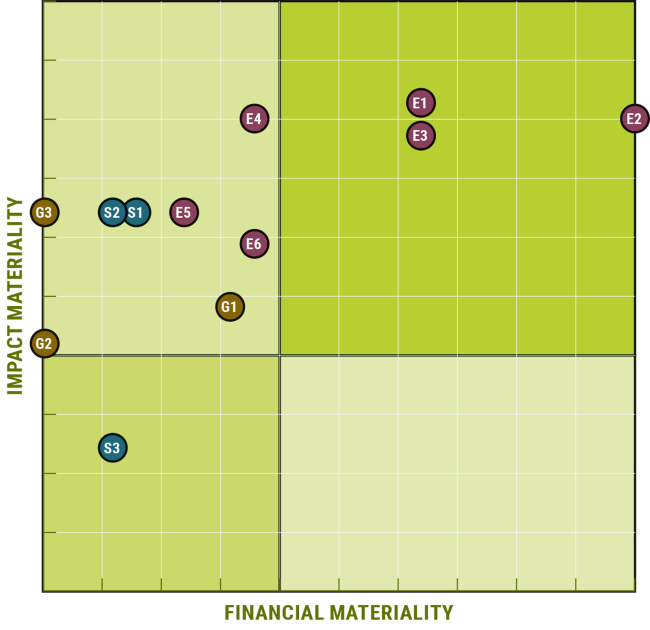
Our materiality analysis evaluates both impact materiality (inside-out) and financial materiality (outside-in). This dual approach ensures that we consider the effects of our operations on the environment and society, as well as the financial implications of ESG factors on our business. By doing so, we can develop a holistic sustainability strategy that addresses the most critical issues.
The methodology for our materiality analysis involved several key steps:
1. Identification of ESG Topics: We identified key ESG areas to be analysed, including Environment (climate change, pollution, water, biodiversity, circular economy), Social (workforce, value chain workers, communities, consumers), and Governance (business conduct).
2. Stakeholder Engagement: We engaged with a diverse group of stakeholders, including customers, suppliers, employees, NGOs, and the Supervisory Board. Next to engaging with customers and suppliers, we analysed public sustainability reports and collected employee feedback across business units.
3. Risk and Opportunity Assessment: We assessed and validated risks, opportunities, and impacts through stakeholder consultations. This process helped us understand the significance of each ESG topic and its relevance to our business and stakeholders.
4. Development of Materiality Matrix: We developed a materiality matrix, which visually represents the priority of identified topics based on their impact and importance.
Stakeholder involvement was an important part of our materiality analysis. We used various methods to gather input, including surveys, interviews, and desk research. The feedback from stakeholders provided valuable insights into their concerns and expectations, which helped us refine our sustainability strategy.
Our materiality assessment resulted in a list of material topics. These topics form the basis of our sustainability strategy and report. To create additional focus, three United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (12, 13, and 17) are selected and form the ‘Faber Development Goals’. We aim to significantly contribute to these SDGs.
The materiality assessment has provided us with a clear understanding of the most critical sustainability topics for our organization and stakeholders. These topics are integrated into our sustainability strategy and guide our actions to achieve our goals. By focusing on the identified material topics, we can effectively manage risks, capitalize on opportunities, and enhance our overall sustainability performance. In the ESG overview we have also highlighted in which policies these topics are addressed.